Quantitative research is the backbone of evidence-based decision-making. By focusing on numerical data and statistical analysis, it allows researchers to measure variables, test relationships, and draw objective conclusions. Whether in business, healthcare, education, or social sciences, quantitative methods provide clarity in understanding patterns, behaviors, and outcomes.
Below, we explore five core quantitative research methods and their real-world applications.
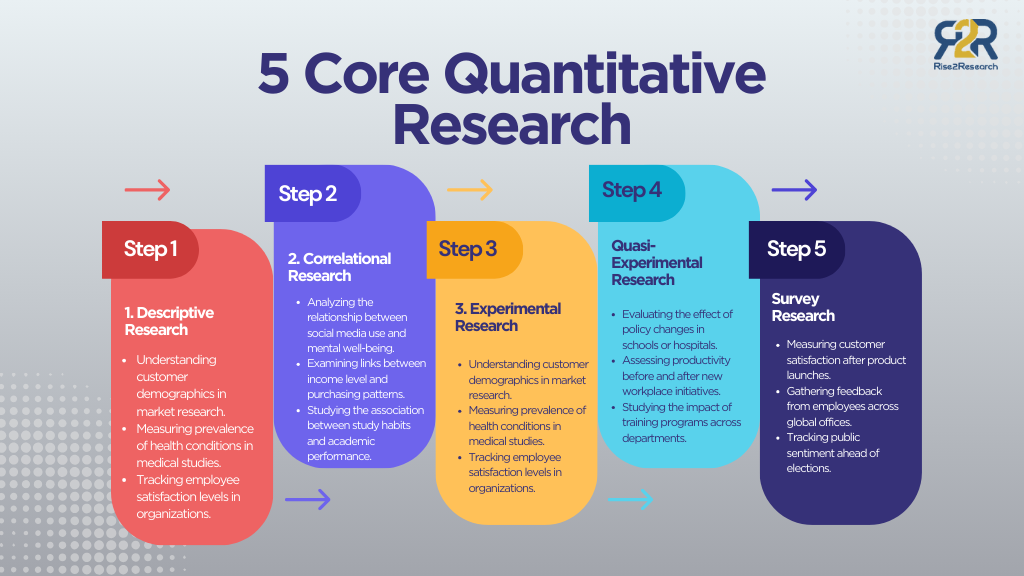
1. Descriptive Research
What it is:
Descriptive research focuses on summarizing and describing characteristics of a population or phenomenon. It doesn’t test cause-and-effect relationships but provides a snapshot of “what is happening.”
Applications:
- Understanding customer demographics in market research.
- Measuring prevalence of health conditions in medical studies.
- Tracking employee satisfaction levels in organizations.
2. Correlational Research
What it is:
This method studies the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them. Correlation doesn’t imply causation, but it shows how strongly variables are connected.
Applications:
- Analyzing the relationship between social media use and mental well-being.
- Examining links between income level and purchasing patterns.
- Studying the association between study habits and academic performance.
3. Experimental Research
What it is:
Experimental research involves manipulating one variable (independent variable) to observe its effect on another (dependent variable) under controlled conditions. This method establishes cause-and-effect relationships.
Applications:
- Testing the effectiveness of a new drug in clinical trials.
- Comparing customer responses to different ad campaigns.
- Measuring the impact of teaching techniques on student outcomes.
4. Quasi-Experimental Research
What it is:
Similar to experimental research but without random assignment of participants. It is often used when controlled experiments are not feasible.
Applications:
- Evaluating the outcomes of policy changes in education or healthcare.
- Studying the impact of community programs where randomization isn’t possible.
- Assessing employee performance before and after organizational changes.
5. Survey Research
What it is:
Survey research gathers quantitative data through structured questionnaires or interviews. It’s one of the most widely used methods for collecting large-scale information.
Applications:
- Measuring customer satisfaction and brand perception.
- Gathering political opinions before elections.
- Collecting feedback on public services or social programs.
Why These Methods Matter
Each of these methods plays a vital role in different stages of research:
- Descriptive → provides the foundation.
- Correlational → reveals relationships.
- Experimental & Quasi-experimental → establish causality.
- Survey → collects large-scale evidence.
By choosing the right method, researchers ensure that their data is reliable, valid, and relevant to the problem at hand.
Also read: Exploring 5 Key Emerging Trends in Qualitative Research
Final Thoughts
Quantitative research methods are powerful tools for uncovering insights and guiding decisions. From understanding trends to testing interventions, these five core approaches provide structured ways to analyze data. The key lies in selecting the right method for the research objective, ensuring results are both meaningful and actionable.